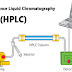
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
HPLC stands for “High-Performance Liquid Chromatography” (sometimes referred to as High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography).High-performance liquid chromatography is a powerful tool in analysis, it yields high performance and high speed compared to traditional columns chromatography because of the forcibly pumped mobile phase.
It is used in biochemistry and analytical chemistry to identify, quantify, and purify the individual components of a mixture.
Advantages of HPLC
- Separations fast and efficient (High-resolution power).
- Continuous monitoring of the column effluent.
- It can be applied to the separation and analysis of very complex mixtures.
- Accurate quantitative measurements.
- Repetitive and reproducible analysis using the same column.
- Adsorption, partition, ion-exchange, and exclusion column separations are excellently made.
- HPLC is more versatile than GLC in some respects because it has the advantage of not being restricted to volatile and thermally stable solute and the choice of mobile and stationary phases is much wider in HPLC.
- Both aqueous and non-aqueous samples can be analyzed with little or no sample pre-treatment.
- A variety of solvents and column packing are available, providing a high degree of selectivity for specific analyses.
- It provides a means for the determination of multiple components in a single analysis.
Applications of High Performance Liquid Chromatography
Pharmaceutical
- Tablet dissolution of pharmaceutical dosages.
- Shelf life determinations of pharmaceutical products.
- Identification of counterfeit drug products.
- Pharmaceutical quality control.
Environmental
- Phenols in drinking water.
- Biomonitoring of PAH pollution in high altitude mountain lakes through the analysis of fish bile.
- Estrogens in coastal waters - the sewage source.
- Toxicity of tetracyclines and their degradation products.
- Assessment of TNT toxicity in sediment.
Forensics
- Identification of anabolic steroids in serum, urine, sweat, and hair.
- Forensic analysis of textile dyes.
- Determination of cocaine and metabolites in meconium.
- Simultaneous quantification of psychotherapeutic drugs in human plasma.
Clinical
- Analysis of antibiotics.
- Detection of endogenous neuropeptides in brain extracellular fluids.
- Increased urinary excretion of aquaporin 2 in patients with liver cirrhosis.
- Quantification of DEET in human urine.
Food and Flavor
- Sugar analysis in fruit juices.
- Stability of aspartame in the presence of glucose and vanillin.
- Ensuring soft drink consistency and quality.